The countdown is on for The British Shooting Show – book tickets online today and save on gate price!
Techniques and skills for hitting the target
 Clay shooting
Clay shooting
Investigating and improving shooting techniques
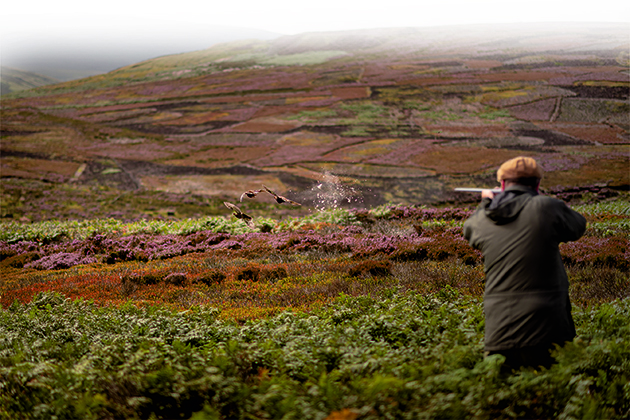
Going-away targets, low incomers and high crossers are what clayshooters frequently want to investigate and improve, namely walked-up and driven grouse and pheasants.
Straight lines
The only targets that do not require the shot pattern to be placed ahead of the clay on its flightline are targets going straight away from you, like a ‘down-the-line clay’ or targets coming straight towards you, such as a clay landing 20 yards out in front. Just shoot straight at them.
The going-away target is usually best shot after giving it a chance to flatten out into a horizontal trajectory. This also means that the target is at a distance where your shot-pellet pattern has had a chance to open up a bit, to say 2ft to 3ft in diameter.
The incoming clay is also best shot when travelling horizontally towards you, before it starts to drop towards the ground.
With both of these targets, the mental confidence to get the timing of the shot correct is fundamental — wait for the opportunity then don’t hesitate, have instinctive confidence; if you check and recheck the target begins to fall and becomes much more complex. With these clays ‘all’ we need to do is sit the clay on top of the rib of the gun and pull the trigger.
The most common fault with these two targets is the tendency to lift the head from the stock to look for the clay; so if you really want to miss the clay — by shooting over the top — delay the shot and lift your head. You should have confidence in your gun mount; keep your head on the stock and get the timing right.
It’s the same with walked-up and straight incoming low grouse. See the target, wait for the flightline to establish and instinctively time the shot, and promptly. The low driven grouse is approaching very quickly and the shot is best accomplished with the bird a good way out in front.
Crossers
So how do you place your shot pattern ahead of the crossing targets?
The answers from various clients show a remarkable variation in each individual’s approach to the challenge:
• “I put more energy into the shot.”
• “I don’t know; I don’t think about it.”
• “I am sort of aware of where my gun
is pointing.”
• “I definitely see the gap between gun and clay. Particularly on long crossers.”
What we are exploring here is the combination of the shooter’s mental approach coupled with their basic understanding of what shooting process they are using, which will lead to suggestions to optimise or improve their shooting techniques.
These quotations are comments from experienced Shots who are pretty good performers and show the shooting techniques that they have acquired, with or without any coaching, ranging from the instinctive to the measured.
If you want to see instinctive, but trained, clay shooting watch the YouTube videos of international skeet competitions on the ISSF website (International Shooting Sports Federation).
The process and timing of the shot does not involve any thinking, but is based on hours of training and repetitive practise of stance, balance, visual pick-up points, gun mount, body rotation and shot placement. The competitor calls ‘pull’ waits for the clay and the process just starts.
Videos of high pheasant and long crossing clay targets seem to show that the expert shooter is almost operating in slow motion and the movements look elegant. There is a rather more deliberate approach to getting the gun on the flight-line of the target, whether its straight or curling, and getting the shot placement in the chosen area ahead of the target. But the key point is the underlying technique has got to be well established.
Shooting techniques
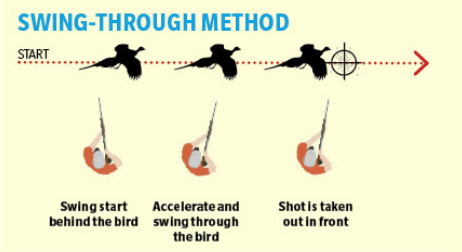
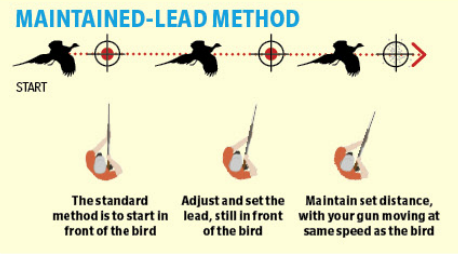
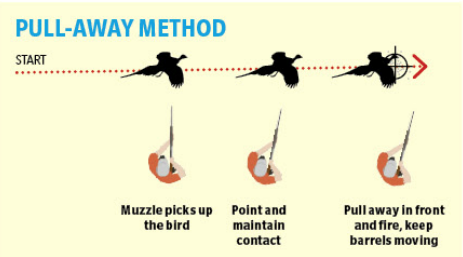
There are only three ways that the pointing of a shotgun can interact with the flightline of a crossing target:
• The gun can start behind the target, catch
it up, overtake and shoot
• Or point at the target then pull ahead
and shoot
• Or move immediately to be ahead of the target and shoot.
The best technique to make your core basic shooting system is the middle process — point at the target and pull ahead. It has many benefits but, fundamentally, your brain knows exactly what is required. If, for example, the target curls, you can keep locked on to it until you wish to pull ahead and shoot.
It is possible to mentally adapt point-and-pull-ahead for use when the timing and target presentation force you into using one of the other two systems.
If you shoot your first target and the position of the second target means you have to swing the gun from behind, don’t react with a chasing slash; move to mentally just touch the second target then pull ahead to shoot. This is much more controlled.
Similarly, the mental approach to a fast pigeon, crossing a rather narrow gap between two woods, is to promptly start gun-mount with solid visual focus on the target, but move to be ahead of the pigeon from the start. That way you are gathering flightline and speed information as the gun mount comes to your cheek and you promptly pull the trigger. This way your brain can try to process all the information benefits of point-and-pull-ahead without the luxury of the actual lock-on with the pigeon. When properly executed, this feels very much like the instinctive shot in Olympic skeet.
Shoot some ordinary English skeet and some long crossers and try to identify where your mental approach and basic technique lie on the spectrum — from really instinctive to definitely measured.
Related Articles
Get the latest news delivered direct to your door
Subscribe to Shooting Times & Country
Discover the ultimate companion for field sports enthusiasts with Shooting Times & Country Magazine, the UK’s leading weekly publication that has been at the forefront of shooting culture since 1882. Subscribers gain access to expert tips, comprehensive gear reviews, seasonal advice and a vibrant community of like-minded shooters.
Save on shop price when you subscribe with weekly issues featuring in-depth articles on gundog training, exclusive member offers and access to the digital back issue library. A Shooting Times & Country subscription is more than a magazine, don’t just read about the countryside; immerse yourself in its most authoritative and engaging publication.